CUPPING AND SCRAPING
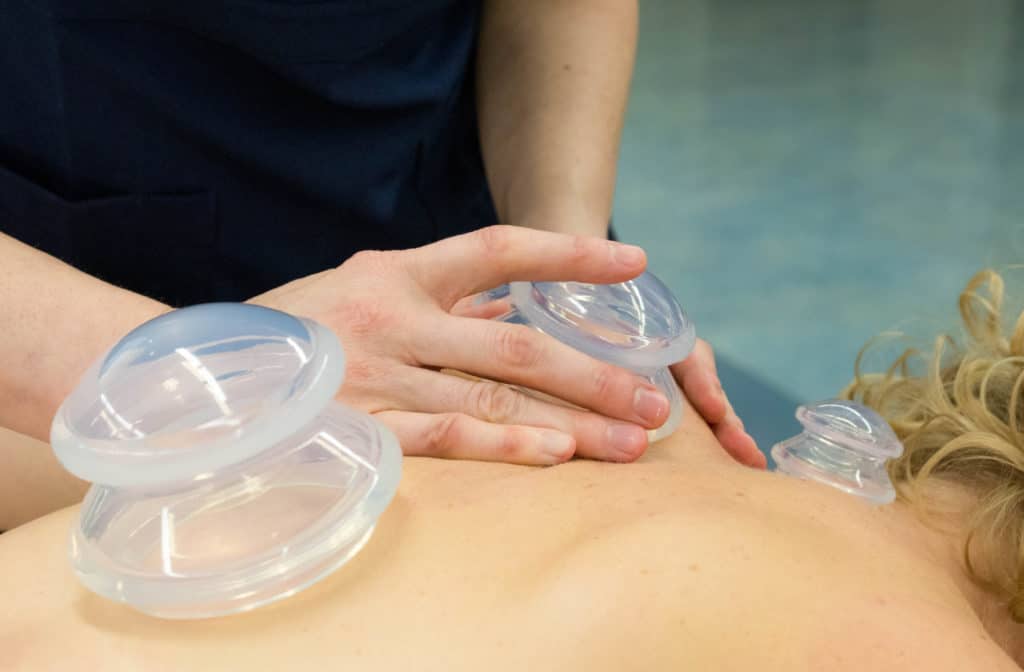
Functional Cupping is an adaptation of an ancient technique. The purpose of this technique is to promote health and healing by loosening soft tissue and connective tissue including scars and adhesions. In addition, it is also thought to improve blood stagnation and increases lymphatic flow and circulation. This therapy can also improve functional mobility and joint performance.
These cups are moved over the skin using gliding, shaking, popping and rotating techniques while gently pulling up on the cup, or may be parked for a short time to facilitate joint mobilization or soft tissue release. Suction reaches deep into the soft tissue and its attachments. Another benefit is to pull toxins and inflammation from the body to the surface of the skin where the lymphatic system can more readily eliminate them.
BENEFITS
- Improve circulation
- Improve muscle flexibility
- Decrease metabolites/inflammation in the area
- Decrease pain
- Create Joint Balance
INDICATIONS
- Hypertonicity
- Inflammation
- Sports Injury
- Neuropathy and nerve pain
- Postural dysfunction
- Chronic injuries
- Edema and poor circulation
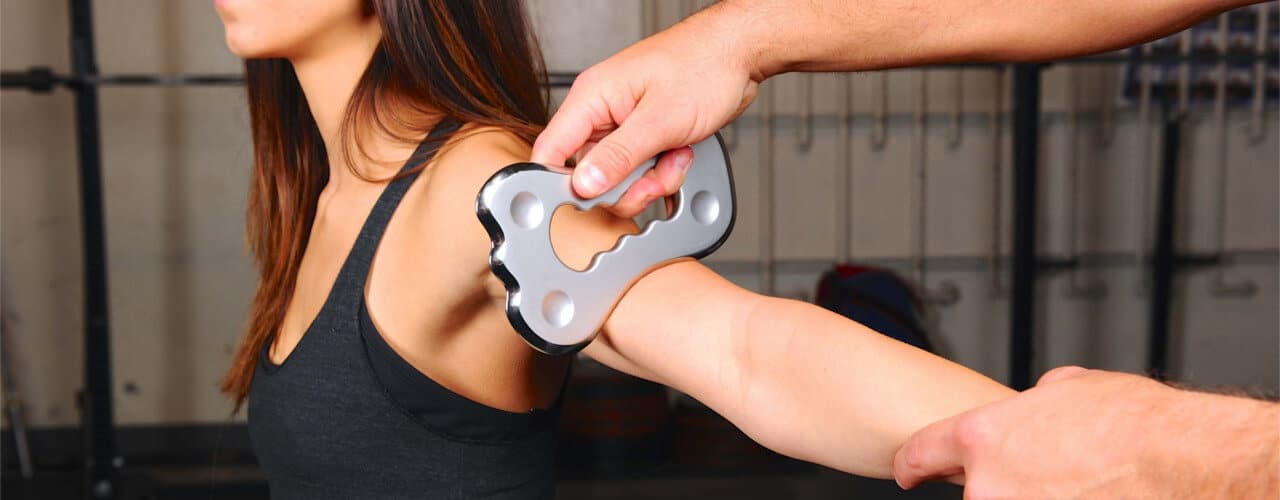

Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) is a process in which the clinician uses a set of hand held instruments to break down the scar tissue and fascial restrictions in soft tissues (muscles, ligaments, tendons, fascia, and nerves). It is a deliberate method of producing microtrauma to stimulate healing. Modernized from the Traditional Chinese Medicine practice called “Gua Sha” which means to scrap away disease by allowing the disease to escape as sand-looking objects through the skin.
BENEFITS
- Breaks down scar tissue
- Promote normal circulation
- Restore movement of fluids as nutrients carried to tissue and metabolic waste carried away
- Facilitation of connective tissue healing
- Release of soft tissue, adhesives, fascial restrictions
- Neuromodulation of pain and tone
INDICATIONS
- Scar Tissue
- Tendinitis
- Sports Injury
- Inflammatory Conditions
- Limits in ROM (joint and Tissue)
- Peripheral neuropathic pain
- Muscle weakness, inhibition
- Hypertonicity

